Why Chrome Crashes (And Why It Keeps Happening)
Chrome crashing is not a rare edge case. It is a routine occurrence for anyone who uses the browser heavily. Understanding the causes helps you both reduce crash frequency and appreciate why external backup is essential.
Cause 1: Memory exhaustion
Chrome runs each tab as a separate process, which improves stability (one tab crashing should not affect others) but increases memory usage. Each tab consumes between 50MB and 300MB of RAM depending on the page content. If you have 40 tabs open, Chrome may be using 4-8GB of memory just for tab processes, not counting extensions, service workers, and Chrome's own overhead.
When your system runs out of available RAM, the operating system may forcefully terminate Chrome processes to free memory. This is the most common cause of sudden Chrome crashes, and it often takes the entire browser down rather than just individual tabs.
Cause 2: Extension conflicts
Chrome extensions run as additional processes and can interact with each other in unexpected ways. A buggy extension can cause memory leaks, infinite loops, or conflicts with Chrome's internal APIs. The more extensions you have installed, the higher the probability of a crash-inducing conflict.
Common culprits include ad blockers processing complex pages, privacy extensions modifying network requests, and development tools injecting code into every page. Even well-written extensions can clash with each other.
Cause 3: Chrome auto-updates
Chrome updates itself automatically in the background. When an update is ready, Chrome needs to restart to apply it. In most cases, Chrome handles this gracefully. But sometimes the update process interrupts the normal session-saving procedure, causing tabs to be lost during the restart.
This is especially problematic because you have no control over when updates happen. Chrome may restart while you are away from your computer, and when you return, your carefully organized workspace is gone.
Cause 4: Corrupted user profile
Chrome stores your settings, bookmarks, extensions, and session data in a user profile directory on your hard drive. Over time, this profile can become corrupted due to improper shutdowns, disk errors, or Chrome bugs. A corrupted profile causes increasingly frequent crashes, and each crash further damages the profile data.
Cause 5: GPU and rendering issues
Chrome uses hardware acceleration (GPU rendering) for better performance. If your GPU drivers are outdated, buggy, or incompatible with certain web content, Chrome can crash during rendering. This type of crash is often sudden and complete, taking down all open tabs simultaneously.
Why Chrome's Built-in Restore Fails After Crashes
Chrome does have session restore built in. So why does it fail when you need it most?
The answer is architectural. Chrome stores its session data in files called Current Session and Current Tabs inside its own profile directory. These files are updated continuously while Chrome is running. When Chrome shuts down normally, it also creates backup files called Last Session and Last Tabs.
The problem is that during a crash, Chrome does not get the chance to properly save these files. The write operation may be interrupted halfway through, leaving the session files corrupted. When Chrome restarts and tries to read these files, it finds unreadable data and falls back to opening a blank page.
| Scenario | Session Files Status | Restore Result |
|---|---|---|
| Normal shutdown | Properly saved | Tabs restored successfully |
| Gentle crash (single tab) | Partially saved | Most tabs restored |
| Hard crash (whole browser) | Corrupted or incomplete | Partial or no restore |
| OS-level kill (out of memory) | Not saved at all | No restore |
| Power loss or forced shutdown | Corrupted | No restore |
| Update restart | Sometimes saved | Unpredictable |
This is a fundamental design problem. Chrome's session restore depends on Chrome being healthy enough to save data. But crashes happen precisely when Chrome is not healthy. The system fails at the exact moment it is needed most.
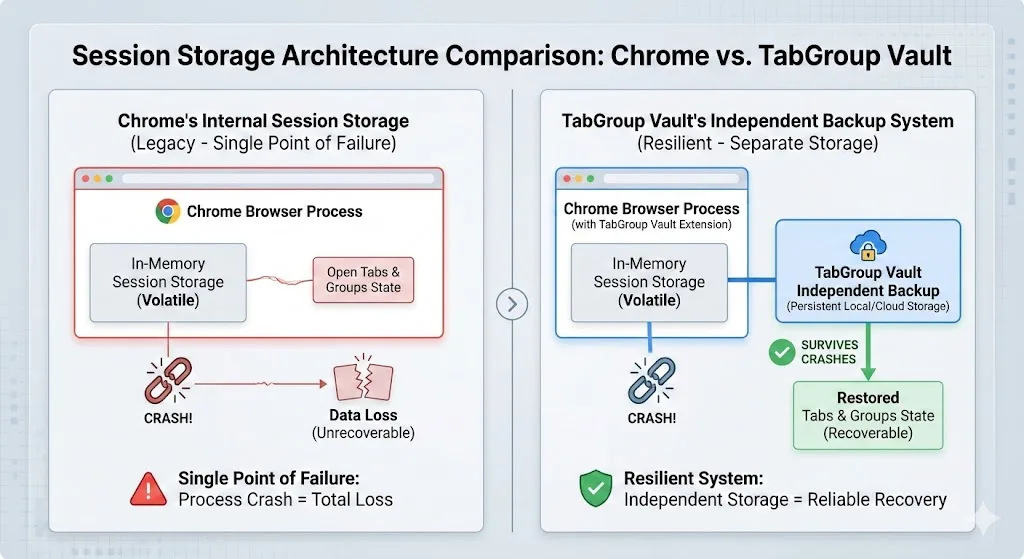
The Permanent Fix: Independent Backup
The solution is straightforward once you understand the problem. If Chrome's internal session storage fails during crashes, the fix is to store your tab data outside of Chrome's internal storage, in a location that Chrome's crashes cannot corrupt.
This is exactly what a well-designed tab backup extension does. Instead of relying on Chrome's session files, the extension maintains its own independent database of your tabs. This database is saved at regular intervals while Chrome is running, so even if Chrome crashes between saves, you lose at most a few minutes of tab changes rather than your entire session.
How independent backup works
- Background monitoring: The extension monitors your open tabs and tab groups continuously.
- Periodic snapshots: At regular intervals, the extension saves a complete snapshot of your current tab state to its own storage.
- Independent storage: The snapshot data is stored in the extension's own storage area, which is separate from Chrome's session files.
- Crash survival: When Chrome crashes, the extension's storage remains intact because it was saved before the crash happened.
- One-click restore: After Chrome restarts, open the extension and restore any saved snapshot with a single click.
TabGroup Vault -- The Permanent Fix
TabGroup Vault stores automatic snapshots of your Chrome tab groups in independent storage that survives any crash. Unlike Chrome's built-in restore, it preserves complete tab group structure -- names, colors, and tab order. When Chrome crashes, open TabGroup Vault and click restore. That is it. Free tier: 5 snapshots. Pro ($29 one-time): unlimited snapshots, bulk restore, Google Drive backup, 5 Chrome profiles.
Reducing Crash Frequency
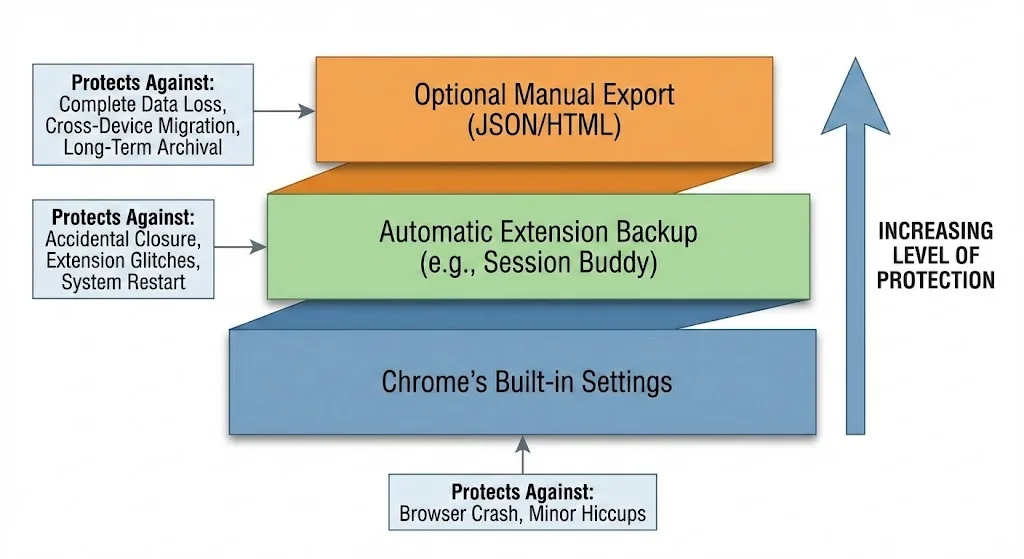
Independent backup is the permanent fix for tab loss, but reducing how often Chrome crashes in the first place also improves your experience. Here are the most effective ways to stabilize Chrome.
Manage memory usage
- Enable Memory Saver: Go to chrome://settings/performance and turn on Memory Saver (also called Tab Discarding). This pauses inactive tabs to free memory.
- Monitor tab count: Use Chrome's built-in Task Manager (Shift+Esc) to see how much memory each tab uses. Close tabs you are not actively using.
- Close heavy tabs: Video streaming, complex web apps, and pages with lots of animations consume disproportionate memory. Close or suspend them when not in use.
Audit your extensions
- Go to chrome://extensions and review every installed extension.
- Disable or remove extensions you do not actively use.
- If Chrome is crashing frequently, try disabling all extensions and re-enabling them one at a time to identify the culprit.
- Keep extensions updated -- outdated extensions are more likely to cause conflicts.
Fix GPU-related crashes
- Update your graphics drivers to the latest version.
- If crashes persist, try disabling hardware acceleration: go to chrome://settings, search for "hardware acceleration," and toggle it off.
- Open chrome://gpu to check for GPU-related warnings or errors.
Reset a corrupted profile
If Chrome crashes frequently regardless of what you do, your user profile may be corrupted. You can create a new profile:
- Click your profile icon in the top-right corner of Chrome.
- Click "Add" to create a new profile.
- Sign in with your Google account to sync bookmarks and settings.
- Install your essential extensions.
- If the new profile is stable, migrate away from the old one.
Before Resetting Your Profile
Make sure you have a backup of your tabs before creating a new profile. If you have TabGroup Vault installed with Google Drive backup enabled, your tab data will automatically be available in the new profile after reinstalling the extension.
The Complete Protection Setup
Here is the recommended configuration for permanent protection against tab loss from Chrome crashes:
Step 1: Install TabGroup Vault (or your preferred backup extension)
This is the most important step. An independent backup extension is the only thing that reliably protects your tabs during crashes. Everything else is supplementary.
Step 2: Enable "Continue where you left off"
Go to chrome://settings/onStartup and select this option. It handles normal shutdowns and works as a first layer of defense.
Step 3: Enable Chrome's Memory Saver
Go to chrome://settings/performance and enable Memory Saver. This reduces memory pressure and makes crashes less frequent.
Step 4: Enable cloud backup (Pro)
If your backup extension supports cloud backup, enable it. This protects against not just Chrome crashes but also hardware failures, OS reinstalls, and device switches.
Step 5: Audit extensions quarterly
Set a calendar reminder to review your installed extensions every three months. Remove what you do not use. Update what you keep. This reduces crash-inducing conflicts over time.
Real-World Impact
Consider the difference between two scenarios:
Without protection: Chrome crashes. You reopen Chrome to a blank page. You spend 20 minutes trying to reconstruct your session from History. You recover most of your tabs but lose all tab group organization. Some pages were behind login walls and you cannot remember the exact URLs. Total disruption: 30-45 minutes plus permanent loss of some context.
With independent backup: Chrome crashes. You reopen Chrome. You click the TabGroup Vault extension icon. You see your most recent snapshot from a few minutes ago. You click "Restore All." Your tabs and tab groups are back exactly as they were. Total disruption: under 30 seconds.
That is the difference between a backup system that lives inside Chrome and one that operates independently. The first fails when Chrome fails. The second keeps working regardless.
Why One-Time Pricing Matters for a Backup Tool
Tab backup is infrastructure. Like a fire extinguisher, you set it up once and it protects you continuously. You should not have to pay monthly for protection that runs automatically in the background.
TabGroup Vault uses a one-time purchase model: $29 for lifetime Pro access. No monthly fees, no annual renewals, no price increases. Compare this with subscription-based alternatives that charge $5-7 per month ($60-84 per year), and the value is clear. You pay once, and your tabs are protected permanently.